New Customer?
Create your accountNo products
Prices are tax included
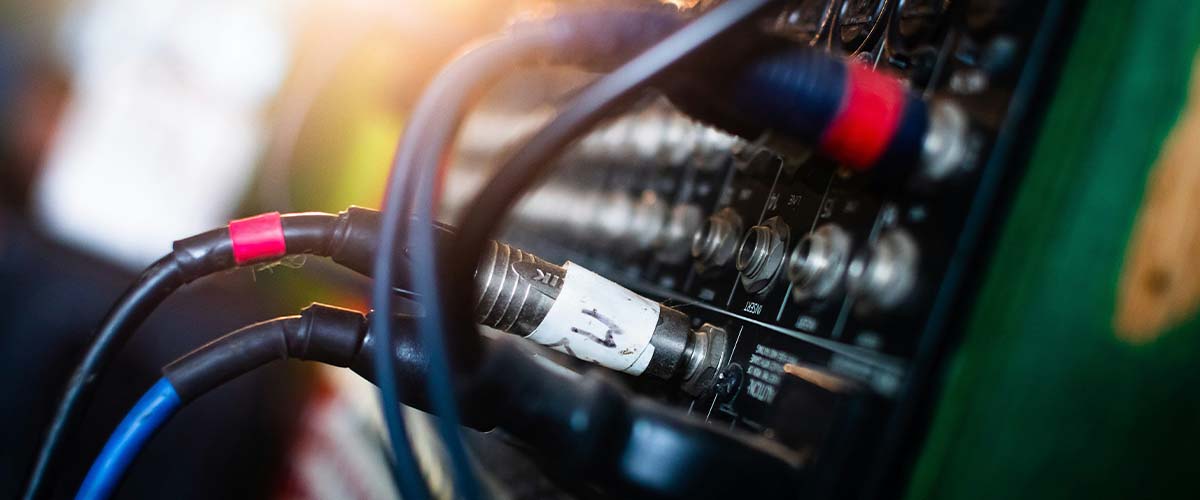
The different jack connector formats

Jack connectors
Various possible applications
The Jack connector format is one of the oldest and most widely used, particularly in the world of music. Introduced at the end of the 18th century for use in telephone exchanges, it has since evolved into several different formats. Historically a 6.35mm jack, today we also find 2.5mm jacks, 3.5mm jacks, 4.4mm jacks and even 5.23mm jacks. But that's not all: a jack connector can be mono, stereo, balanced or unbalanced. So how do you choose the right jack connector?
History of the Jack connector
The invention of the Jack connector dates back to 1877. This connector was invented as part of the installation of the first telephone exchanges. The 6.35mm jack format, even though other formats such as the 4.4mm jack already existed, became the standard in terms of telephone line connectivity. At the time, it was nicknamed the "phone plug" and was mainly used by switchboard operators, before its use gradually became more widespread. Indeed, thanks to its low manufacturing cost, it was used on amplifiers and electric guitars as early as the 1930s. The miniature 3.5mm jack version was introduced in the 1950s for the headphones of transistor radios, popularized by the famous SONY EFM-117J radio released in 1964, then by the first Walkman, again from Japanese brand Sony, in 1979. The 2.5mm jack was also used for small electronic devices. It can be used to transmit audio, but also a video signal in certain cases. Less conventional and less well-known formats such as the 5.23mm and 7.14mm jacks are generally used by the military for telecommunications, as well as by the aviation sector.

Different jack plug formats
Jack 6.35mm (1/4″)
The 6.35mm jack plug is still widely used, thanks to its robustness. In fact, it's the plug of choice for connecting electric guitars and basses, and therefore the socket of amplifiers, effects pedals and USB interfaces commonly known as "sound cards". On the Hi-Fi side, it's mainly used for connecting some headphones.


Jack 4.4mm
The 4.4mm jack, also known as Bantam, is mainly used for balanced headphone connections and professional audio connectors. This format is still widely used thanks to the Pentaconn standard, which makes it balanced with no less than five contact pins.
Jack 3.5mm (mini-jack)
A standard connector, the 3.5mm jack is still widely used for earphones, headphones and active desktop speakers for use with a phone, tablet or computer. In recent years, it has tended to fade slightly, as the standard for phones evolves towards a USB-C connection even for transferring audio signals.


Jack 2.5mm (subminiature)
Rarely used these days, because its small size makes it too fragile, the 2.5mm jack was once used for headphones or to power small devices. In Hi-Fi, however, it is found on the connectors of small devices such as portable DAC/headphone amplifiers, to save space and keep a small form factor.
Mono, stereo, unbalanced, balanced: TS/TRS/TRRS/TRRRS standards
Today, all formats are available in mono, stereo, balanced and unbalanced versions. However, due to specific standards, balanced jacks are often in 4.4mm jack or 2.5mm jack format, while 6.35mm jack and 3.5mm jack formats are used for mono or unbalanced stereo.
To distinguish the different types of connection possible, we use the TS/TRS/TRRS/TRRRS standards. "T" for "Tip", "R" for "Ring" and "S" for "Sleeve". This designation simply determines the number of contacts on a jack connector, whether in 6.35mm, 4.4mm, 3.5mm or 2.5mm format.
TS standard: 2 contact points
The 2-contact jack is generally used to transmit a monophonic signal. There is one contact for the signal (Tip) and one for ground (Sleeve - GND).
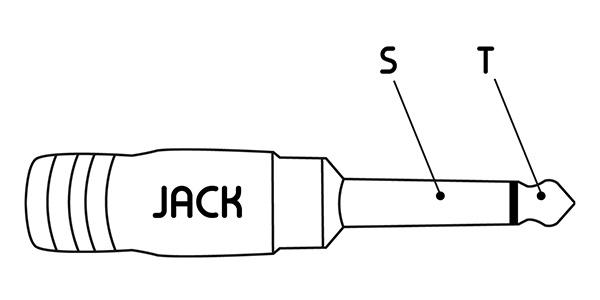
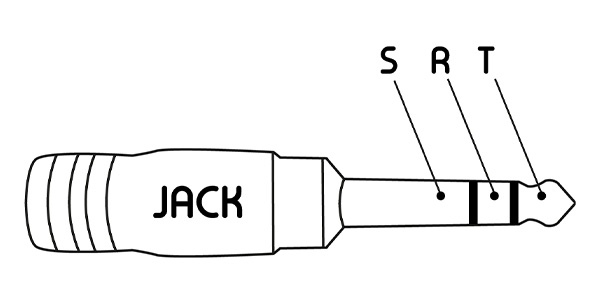
TRS standard: 3 contact points
Jack connectors with 3 contact points can be used for a variety of purposes:
- Transmit stereo sound. "Tip" for the left channel, "Ring" for the right channel and "Sleeve" for ground.
- Transmitting a balanced mono signal, such as an XLR modulation cable. Tip" for the hot point, "Ring" for the cold point and "Sleeve" for ground.
TRS jack connectors are the most widely used on the market today. They are also widely used in professional applications, such as the insert function on mixing consoles.
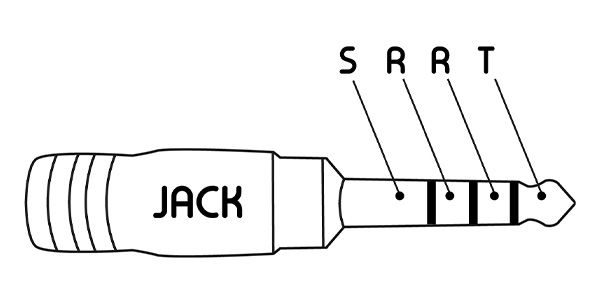
TRRS standard: 4 contact points
TRRS jack connectors are generally used to transmit stereo sound and add a function such as a microphone or video signal. However, there is no standard pin placement for this type of connector. So always check compatibility with your device before using this type of connection.
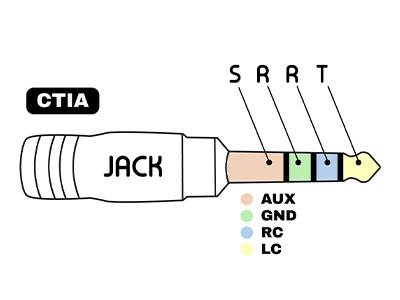
For headphones and earphones with microphones, there are two main standards: CTIA (The Wireless Association) and OMTP (Open Mobile Terminal Platform). The difference between these two standards lies in the location of the microphone contact (AUX) and ground (GND), as shown in the diagram below. The CTIA standard is still the most commonly used today.
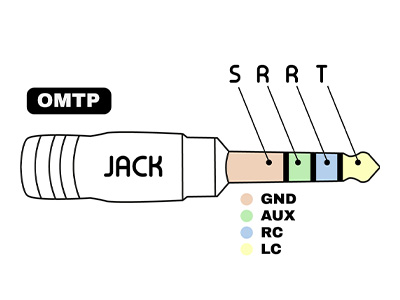
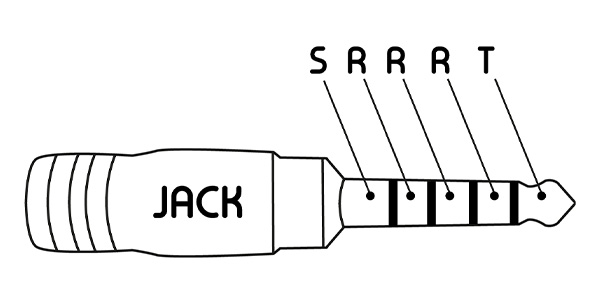
TRRRS standard: 5 contact points
TRRRS connectors are mainly used to transmit balanced stereo signals. This is the Pentaconn standard for the 4.4mm jack. TRRRS is also often used on 2.5mm jacks for balanced connections. The connection is shown below:
- Tip: left channel (+)
- Ring: left channel (-)
- Ring: right channel (+)
- Ring : right channel (-)
- Sleeve : ground
The replacement of the 3.5mm jack connector with USB-C on smartphones
Recently, many devices, such as the latest generation of smartphones, have tended to do away with their jack output in order to reduce their thickness. This has led to the emergence of earphones with USB-C connectors for transmitting audio signals.
The main question on most users' minds is: how am I going to listen to music and charge my phone at the same time? In the end, the answer is quite simple. All you need is a Y adapter and you're ready to go!
So what are the advantages of USB-C? There's the fact that DAC chips, DSPs and amplifiers will now be positioned on the side of headphone and earphone manufacturers. This means we'll have to worry more about buying headphones that we can make last over time, while still being able to change smartphones without affecting listening quality.
USB-C audio is promoted by Intel, which is nonetheless aware of the obstacles encountered in the 3.5mm jack/USB-C transition. That's why the company is even considering enabling analog transmission via USB-C for a smoother transition phase before going "all digital". However, as far as Hi-Fi equipment is concerned, this type of connection is still far from being replaced.
Rechercher dans le blog
Blog categories
Latest Comments
Audiophonics Team
on DIY Tutorial - PiCorePlayer - Installing...Pierre Bommel
on Lecteur réseau Opensource : SolutionsPierre Bommel
on DIY Tutorial - PiCorePlayer - Installing...Audiophonics Team
on Tutorial DIY - Power cable ELECAUDIO CS-331B






























